快速熟悉常用的数据结构以及它们的应用场景,了解常用算法的模板。
数据结构
线性结构
数组 Array
- 内存连续,适合较少的相同类型的数据
- 支持随机访问,通过索引快速访问数据,时间复杂度为
O(1)
- 遍历查找元素的时间复杂度为
O(n)
- 插入删除元素的时间复杂度为
O(n)
适合读操作多的场景。
循环数组
TODO
链表 List
- 内存分散,通过指针指向下一个节点,可用于较多的相同类型的数据
- 遍历查找元素的时间复杂度为
O(n)
- 支持快速插入删除,时间复杂度为
O(1)
适合写操作多的场景。
堆栈/栈 Stack && 队列 Queue
应用场景:
线性结构的双指针遍历
前后指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
|
快慢指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
|
头尾指针向中间靠拢
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| int l = i + 1;
int r = nums.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int total = cur + nums[l] + nums[r];
if (total == 0) {
...
++l;
--r;
} else if (total > 0){
--r;
} else {
++l;
}
}
|
优先队列 PriorityQueue
对输入的元素进行排序,按照优先级来输出。
常见的应用场景:
哈希 Hash
常见的应用场景:
- 唯一性快速查找对象,先进行
hash 哈希比较,然后 equal 等值比较
二叉树 && 图
每个节点都包含以下信息:
二叉搜索树 BST
特点:
- 左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
- 右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
- 左右子树也都满足 BST 的特点
对 BST 进行中序遍历,可以构成一个有序数组。
平均查询时间复杂度 O(logN),但 BST 不是一个自平衡的树,最坏情况下会退化成链表,导致时间复杂度为 O(N)。
平衡二叉树 AVL
平衡二叉树是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
高度=从当前节点到子树中最远叶子节点的最长路径上的边数,即该路径上的节点数 - 1,可通过层级遍历计算。
树的高度就等于根节点的高度。
当不平衡时,需要通过旋转来调平二叉树。
2-3 树 && 红黑树
红黑树是使用二叉树对 2-3 树的一种实现,它并不追求严格的平衡,而是大致的平衡。
- 根节点必为黑色
- 节点颜色有红色和黑色,红色节点和其黑色父节点结合起来,相当于 2-3 树中的一个节点
- 所有叶子节点都是黑色
- 任意节点到叶子节点经过的黑色节点数目相同,只有黑色节点才贡献高度值
- 不会有连续的红色节点,红色节点必要要和黑色父节点结合才有意义
节点中的每条边决定了要查找的数据的范围。
红黑树在最坏的情况下查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度始终是 O(logN)。
Rerefence:
平衡多路查找树 (B/B+ 树)
TODO
字典树 Trie
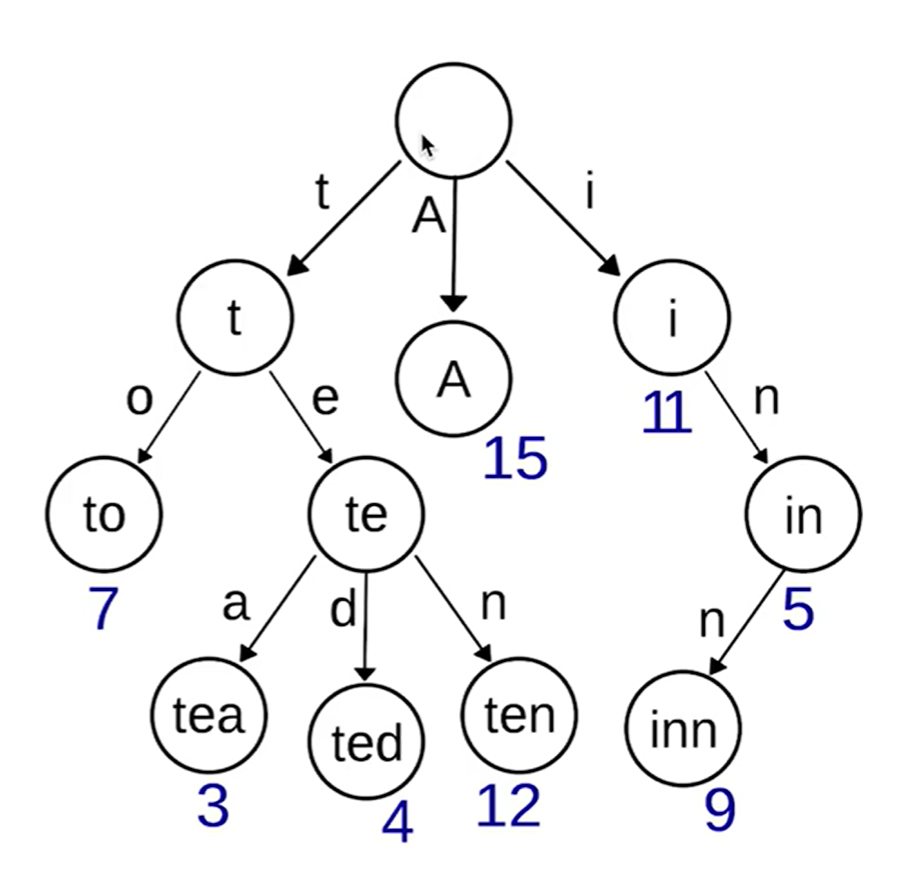
树形结构,通过每个节点的边来维护公共前缀字符串,即键值。
利用公共前缀来降低查询时间的开销以提高查询效率。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| class Trie {
private final Trie[] children;
private boolean isEnd;
public Trie() {
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
public void insert(String word) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
int index = ch - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
Trie node = searchPrefix(word);
return node != null && node.isEnd;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(prefix) != null;
}
private Trie searchPrefix(String prefix) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char ch = prefix.charAt(i);
int index = ch - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
return null;
}
node = node.children[index];
}
return node;
}
}
|
应用场景:
- 基于前缀的搜索/推荐
- 搜索引擎的文本词频统计以及搜索
倒排索引
TODO
遍历方式
- 前序遍历,根左右
- 中序遍历,左根右
- 后序遍历,左右根
- 层级遍历
广度遍历 BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.addLast(root);
var result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int count = queue.size();
List<Integer> layer = new ArrayList<>(count);
while (count-- != 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.removeFirst();
layer.add(node.val);
if (Objects.nonNull(node.left)) {
queue.addLast(node.left);
}
if (Objects.nonNull(node.right)) {
queue.addLast(node.right);
}
}
result.add(layer);
}
|
深度遍历 DFS
计算机一般使用 DFS 来解决问题,例如堆栈的使用。
- 终止条件
- 计算结果的获取
- 对子节点的遍历,可以使用剪枝来优化遍历
- 节点状态,可选
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| private int dfs(TreeNode node, Long preSum, Map<Long, Integer> preSums, int targetSum) {
if (node == null) {
return 0;
}
preSum = preSum + node.val;
int count = preSums.getOrDefault(preSum, 0) + 1;
preSums.put(preSum, count);
int ret = preSums.getOrDefault(preSum - targetSum, 0);
ret += dfs(node.left, preSum, preSums, targetSum);
ret += dfs(node.right, preSum, preSums, targetSum);
preSums.put(preSum, count - 1);
return ret;
}
|
并查集 union & find
- 初始化,每个元素的 root 指向自己或者用flag标记为root
- Union,合并关联数据
- Find
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| public class UnionFind {
private final int[] roots;
public UnionFind(int n) {
roots = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
roots[i] = i;
}
}
private int find(int i) {
int root = i;
while (root != roots[root]) {
root = roots[root];
}
while (i != roots[i]) {
int next = roots[i];
roots[i] = root;
i = next;
}
return root;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pr = find(p);
int qr = find(q);
roots[pr] = qr;
}
public boolean isConnected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
}
|
- Union 优化:将深度较小的元素的 root 作为另一个元素的 root 的 root。
- Find 优化:对路径进行压缩,使路径的深度不会过大
应用场景:
跳表
跳表可以理解为在链表基础上,建立多级索引,通过多级索引检索定位将增删改查的时间复杂度变为 O(logN) 。
查询的主要过程是定位到小于要查的 value 的最大值的节点,
从跳表最高级的索引开始定位,找到该索引中小于要查的 value 的最大值的节点,
然后继续定位到该节点的下一级索引,继续之前的查找操作。
Reference:
布隆过滤器 Bloom Filter
通过映射函数(类似哈希函数)映射到二进制向量中,用于检索一个元素是否在一个集合中。
如果它判断出不在,则该元素一定不在集合中;
如果判断出存在,则该元素不一定在集合中,因为可能存在映射冲突,多个元素的映射值相同,但元素不相同。
主要用于识别元素不存在集合中。
遍历技巧
剪枝
在遍历过程中,对不必要的节点进行过滤,提高遍历的效率。
递归 && 分治
把一个大的问题分解为相同的小问题,对每个小问题进行求解,最后合并得到最终的结果。
动态规划
必要元素:
- 状态定义,定义要保存哪些结果数据用于后续推导
- 状态转移方程/递推公式,基于之前的结果来推导现有的结果。可以先用 递归 + 状态 来思考,然后转换为 递推(循环)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] result = new int[n + 1];
result[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == 1) {
result[i] = 1;
continue;
}
if (i == 2) {
result[i] = 2;
continue;
}
result[i] = result[i - 2] + result[i - 1];
}
return result[n];
}
|
常见的优化技巧
位运算



排序
快速排序
TODO
搜索
二分查找
前提条件:
- 元素有序性, 单调递增或者递减
- 有界,存在上下界
- 可通过索引访问,一般用于数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
public int mySqrt(int x) {
int left = 0;
int right = x;
int ans = -1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if ((long) mid * mid <= x) {
ans = mid;
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
private boolean search(int[] row, int target) {
int l = 0;
int r = row.length - 1;
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (row[m] == target) {
return true;
}
if (row[m] < target) {
l = m + 1;
} else {
r = m - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
|
查找链表的中间节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| ListNode pre = head;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
|
其他应用场景
前缀和
主要用于求解任意区间的子序列和。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| private static int[] getRange(int avg, int[] nums) {
int[] preSum = new int[nums.length + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= nums.length; i++) {
preSum[i] = preSum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
int[] result = new int[0];
int maxLen = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int end = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j <= nums.length; j++) {
int sum = preSum[j] - preSum[i];
int len = j - i;
int lost = len * avg;
if (sum > lost) {
break;
}
end = j;
}
int curLen = end - i;
if (curLen == 0) {
continue;
}
if (curLen <= maxLen) {
continue;
}
result = new int[] {i, end};
maxLen = curLen;
}
return result;
}
|
滑动窗口
- (常用)使用 queue 来构建有序队列。
- 针对数组,还可以使用双指针来确定窗口的范围。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>(k);
...
int[] rst = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
for (int i = k - 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (!queue.isEmpty() && nums[queue.getLast()] <= nums[i]) {
queue.removeLast();
}
queue.addLast(i);
int start = i - k + 1;
while (queue.getFirst() < start) {
queue.removeFirst();
}
rst[start] = nums[queue.getFirst()];
}
|
LRU Cache
LRU(Least Recently Usage) 指最近最少使用的缓存策略。
可以使用双向链表来实现,将最近使用的放在头部,而最近最少使用的会放在尾部,
当缓存满的时候,会将尾部最近最少使用的元素移除。
- 头部查询时间复杂度 O(1)
- 尾部删除时间复杂度 O(1)
实现思路版本,任何语言都可以参考。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| class LRUCache {
private final LinkedList<Integer> keys;
private final HashMap<Integer, Integer> cache;
private final int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
keys = new LinkedList<>();
cache = new HashMap<>(capacity);
}
public int get(int key) {
if (!cache.containsKey(key)) {
return -1;
}
mvToNewest(key);
return cache.get(key);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if (cache.containsKey(key)) {
mvToNewest(key);
cache.put(key, value);
return;
}
keys.addFirst(key);
cache.put(key, value);
if (keys.size() > capacity) {
Integer oldestKey = keys.removeLast();
cache.remove(oldestKey);
}
}
private void mvToNewest(int key) {
keys.remove(Integer.valueOf(key));
keys.addFirst(key);
}
}
|
Java 可以借助 LinkedHashMap 来实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> {
private int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
super(capacity, 0.75F, true);
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
return super.getOrDefault(key, -1);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
super.put(key, value);
}
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Entry<Integer, Integer> eldest) {
return size() > capacity;
}
}
|
双指针确定边界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length <= 2) {
return nums.length;
}
int l = 2;
for(int r = 2; r < nums.length; r++) {
if (nums[r] != nums[l - 2]) {
nums[l] = nums[r];
++l;
}
}
return l;
}
|
Reference



